Two Notation Systems for Signed Languages: Stokoe Notation & Sutton SignWriting Joe Martin Western Washington University Martinj4@cc.wwu.edu |
||||||||||||
|
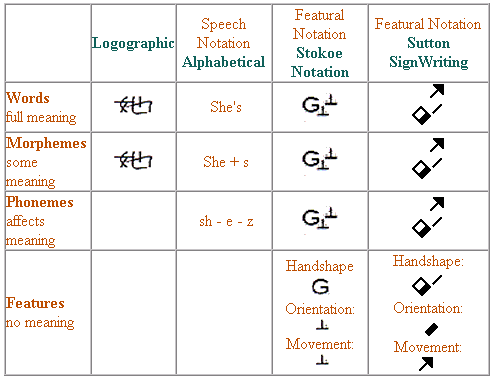
A notation is any set of symbols used to denote things, including mathematics. A writing system is a notation for representing the structure of a language; alphabets and syllabaries are writing systems. A script is the particular collection of symbols used to make a writing system visible. Our Roman Alphabet is a script, as are SSW, SN, the Japanese syllabary, and Chinese Characters. An orthography is specific to one language. Spanish, German and French are all written in the same script but have different orthographies. Both SSW and SN are scripts, used to write any number of signed languages. People call them alphabets, but technically this is not correct. Different types of scripts are classified by what level of language they match their symbols to. Chinese writing matches its symbols with the word level, using a symbol for each morpheme. We call this a logographic script. Below the word/morpheme level is one built of smaller parts called phonemes (in spoken languages these are the sound segments). Alphabets assign symbols to this level. Below that is the level built of the even smaller phonetic features. Feature notation assigns symbols at this level, and that is what both SSW and SN do, as Figure 4 illustrates.
Logographic Chinese writing has no symbols for anything smaller than the morpheme, alphabets have no symbols for anything smaller than a phoneme, but both SN and SSW have symbols even for features: they are not alphabets. |
||||||||||||
|